
Last week a new piece of Parkinson’s disease research has been widely discussed in the media.
It involves Hepatitis – the viral version of it at least.
In today’s post we will review the research and discuss what it may mean for Parkinson’s disease.

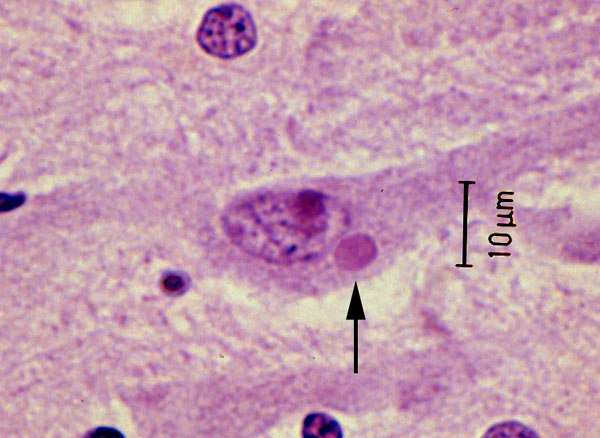
A lewy body (brown with a black arrow) inside a cell. Source: Cure Dementia
A definitive diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease can only be made at the postmortem stage with an examination of the brain. Until that moment, all cases of Parkinson’s disease are ‘suspected’.
Critical to that postmortem diagnosis is the presence of circular shaped, dense clusters of proteins, called Lewy bodies (see the image above for a good example).
What causes Lewy bodies? We don’t know, but many people have theories.
This is Friedrich Heinrich Lewy (1885-1950).
Friedrich Lewy. Source: Lewy Body Society
As you can probably guess, Friedrich was the first to discover the ‘Lewy body’. His finding came by examining the brains of 85 people who died with Parkinson’s disease between 1908 – 1923.
In 1931, Friedrich Lewy read a paper at the International Congress of Neurology in Bern. During that talk he noted the similarities between the circular inclusions (called ‘negri bodies’) in the brains of people who suffered from rabies and his own Lewy bodies (observed in Parkinson’s disease).
A Negri body in a cell affected by rabies (arrow). Source: Nethealthbook
Given the similarities, Lewy proposed a viral cause for Parkinson’s disease.
Now, the idea that Parkinson’s disease could have a viral component has existed for a long time – even before Lewy made his conclusion. As we have previous mentioned, theories of viral causes for Parkinson’s have been circulating ever since the 1918 flu pandemic (Click here to read our post on this topic).

An example of post-encephalitic Parkinsonism. Source: Baillement
About the same time as the influenza virus was causing havoc around the world, another condition began to appear called ‘encephalitis lethargica‘ (also known as post-encephalitic Parkinsonism). This disease left many of the victims in a statue-like condition, both motionless and speechless – similar to Parkinson’s disease. Initially, it was assumed that the influenza virus was the causal factor, but more recent research has left us not so sure anymore.
Since then there, however, has been additional bits of evidence suggesting a viral role in Parkinson’s disease. Such as this report:

Title: Highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus can enter the central nervous system and induce neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration.
Author: Jang H, Boltz D, Sturm-Ramirez K, Shepherd KR, Jiao Y, Webster R, Smeyne RJ.
Journal: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009 Aug 18;106(33):14063-8.
PMID: 19667183
The researchers in this study found that when they injected the highly infectious H5N1 influenza virus into mice, the virus progressed from the periphery (outside the brain) into the brain itself, where it induced Parkinson’s disease-like symptoms. The virus also caused a significant increase in the accumulation of the Parkinson’s associated protein Alpha Synuclein. Importantly, they witnessed the loss of dopamine neurons in the midbrain of the mice 60 days after resolution of the infection – that cell loss resembling what is observed in the brains of people with Parkinson’s disease.
The Parkinson’s associated protein alpha synuclein has also recently demonstrated anti-viral properties:

Title: Alpha-Synuclein Expression Restricts RNA Viral Infections in the Brain.
Authors: Beatman EL, Massey A, Shives KD, Burrack KS, Chamanian M, Morrison TE, Beckham JD.
Journal: J Virol. 2015 Dec 30;90(6):2767-82. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02949-15.
PMID: 26719256 (This article is OPEN ACCESS if you would like to read it)
David Beckham (not the football player) and his research colleagues introduced West nile virus to brain cells grown in cell culture and they observed an increase in alpha synuclein production. They also found that the brains of people with West nile infections had increased levels of alpha synuclein.
The researchers then injected West Nile virus into both normal mice and genetically engineered mice (which produced no alpha synuclein) and they found that the genetically engineered mice which produced no alpha synuclein died quicker than the normal mice. They reported that there was an almost 10x increase in viral production in the genetically engineered mice. This suggested to them that alpha synuclein may be playing a role in protecting cells from viral infections.
Interesting, but what about this new data involving Hepatitis?
Yes, indeed. Let’s move on.
Wait a minute, what is Hepatitis exactly?
The name Hepatitis comes from the Greek: Hepat – liver; and itis – inflammation, burning sensation. Thus – as the label suggests – Hepatitis is inflammation of liver tissue.

Hepatitis and the liver. Source: HealthandLovepage
It can be caused by infectious agents (such as viruses, bacteria, and parasites), metabolic changes (induced by drugs and alcohol), or autoimmune/genetic causes (involving a genetic predisposition).
The most common cause of hepatitis is viral.
There are five main types of viral hepatitis (labelled A, B, C, D, and E). Hepatitis A and E are mainly spread by contaminated food and water. Both hepatitis B and hepatitis C are commonly spread through infected blood (though Hepatitis B is mainly sexually transmitted). Curiously, Hepatitis D can only infect people already infected with hepatitis B.
Hepatitis A, B, and D are preventable via the use of immunisation. A vaccine for hepatitis E has been developed and is licensed in China, but is not yet available elsewhere
Hepatitis C, however, is different.
There is currently no vaccine for it, mainly because the virus is highly variable between strains and the virus mutates very quickly, making an effective vaccine a difficult task. A number of vaccines under development (Click here for more on this).
What is known about Hepatitis C and the brain?
Quite a bit.
Similar to HIV (which we discussed in a previous post), the hepatitis C virus (HCV) enters the brain via infected blood-derived macrophage cells. In the brain, it is hosted by microglial cells, which results in altered functioning of those microglial cells. This causes problems for neuronal cells – including dopamine neurons. For example, people infected with HCV have reduced dopamine transmission, based on brain imaging studies (Click here and here for more on this result).
Have there been connections between hepatitis C virus and Parkinson’s disease before?
Yes.

Title: Hepatitis C virus infection: a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease.
Authors: Wu WY, Kang KH, Chen SL, Chiu SY, Yen AM, Fann JC, Su CW, Liu HC, Lee CZ, Fu WM, Chen HH, Liou HH.
Journal: J Viral Hepat. 2015 Oct;22(10):784-91.
PMID: 25608223
The researchers in this study used data collected from a community-based screening program in north Taiwan which involved 62,276 people. The World Health Organisation (WHO) estimates that the prevalence of hepatitis C viral infection worldwide is approximately 2.2–3%, representing 130–170 million people. Taiwan is a high risk area for hepatitis, with antibodies for hepatitis viruses in Taiwan present in 4.4% in the general population (Source).
The researchers found that the significant association between hepatitis C viral infections and Parkinson’s disease – that is to say, a previous infection of hepatitis C increased the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease (by 40%). The researchers then looked at what the hepatitis C and B viral infections do to dopamine neurons growing in cell culture. They found that hepatitis C virus induced 60% dopaminergic cell death, while hepatitis B had no effect.
This study was followed up a few months later, by a second study suggesting an association between Hepatitis C virus and Parkinson’s disease:

Title: Hepatitis C virus infection as a risk factor for Parkinson disease: A nationwide cohort study.
Authors: Tsai HH, Liou HH, Muo CH, Lee CZ, Yen RF, Kao CH.
Journal: Neurology. 2016 Mar 1;86(9):840-6.
PMID: 26701382
The researchers in this study wanted to investigate whether hepatitis C could be a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. They did this by analyzing data from 2000-2010 drawn again from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database.
The database included 49,967 people with either hepatitis B, hepatitis C or both, in addition to 199,868 people without hepatitis. During the 12 year period, 270 participants who had a history of hepatitis developed Parkinson’s disease (120 still had hepatitis C). This compared with 1,060 participants who were free of hepatitis, but went on to develop Parkinson’s disease.
When the researchers controlled for potentially confounding factors (such as age, sex, etc), the researchers found participants with hepatitis C had a 30% greater risk of developing Parkinson’s disease than the controls.
So if this has been demonstrated, why is this new study last week so important?
Good question.
The answer is very simple: This study is not based on statistics from Taiwan – this new study has found the same result from a new population.

Title: Viral hepatitis and Parkinson disease: A national record-linkage study.
Authors: Pakpoor J, Noyce A, Goldacre R, Selkihova M, Mullin S, Schrag A, Lees A, Goldacre M.
Journal: Neurology. 2017 Mar 29. [Epub ahead of print]
PMID: 28356465
These researchers used the English National Hospital Episode Statistics database and linked it to mortality data collected from 1999 till 2011. They too have found a strong association between hepatitis C and Parkinson’s disease (standardized rate ratio 1.51, 95% CI 1.18–1.9).
Curiously (and different from the previous studies), the researchers in this study also found a strong association for hepatitis B and Parkinson’s disease (standardized rate ratio 1.76, 95% CI 1.28–2.37). And these associations appear to be specific to Hepatitis B and C, as the investigators did not find any association between autoimmune hepatitis, chronic hepatitis, or HIV.
One important caveat with this new study, however, is that the authors could not
control for lifestyle factors (such as smoking or alcohol consumption). In addition, their system of linking medical records may underestimate the numbers of patients with
Parkinson’s disease as it would not take into account people with Parkinson’s disease who do not seek medical advice or those who are misdiagnosed (given a wrong diagnosis – it does happen!).
Regardless of these cautionary notes, the results still add to the accumulating evidence of an association between the virus that causes Hepatitis and the neurodegenerative condition of Parkinson’s disease.
But what about those people with Parkinson’s disease who have never had Hepatitis?
Yeah, this is a good question.
But there is a rather uncomfortable answer to it.
Here’s the rub: “Approximately 70%–80% of people with acute Hepatitis C do not have any symptoms” (Source: Centre for Disease Control). That is to say, the majority of people infected with the Hepatitis C virus will not be aware that they are infected. Some of those people who are infected may think that they have a case of the flu (HCV symptoms include fever, fatigue, loss of appetite,…), while others will simply not display any symptoms at all.
So many people with Parkinson’s disease may have had HCV, but never been aware of it.
And this is the really difficult part of researching the causal elements of Parkinson’s disease.
The responsible agent may actually leave little or no sign that they were ever present. For a long time, people have suggested that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a thief in the night – some agent that comes in, causes a problem and disappears without detection.
Perhaps Hepatitis is that thief.
But hang on a second, 60–70% of HCV infected people will go on to develop chronic liver disease (Source). Do people with Parkinson’s disease have liver issue?
Umm, well actually, in some cases: yes.
There have been studies of liver function in Parkinson’s disease where abnormalities have been found (Click here for more on this). And dopamine cell dysfunction has been seen in people with cirrhosis issues (Click here for more on this). In fact, the prevalence of Parkinsonism in people with cirrhosis has been estimated to be as high as 20% (and Click here for more on that).
So what are we saying? Hepatitis causes Parkinson’s disease???
No, we are not saying that.
Proving causality is the hardest task in science.
In addition, there have been a few studies in the past that have looked at viral infections as the cause of Parkinson’s disease that found strong associations with other viruses. For example this study:
Title: Infections as a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease: a case-control study.
Authors: Vlajinac H, Dzoljic E, Maksimovic J, Marinkovic J, Sipetic S, Kostic V.
Journal: Int J Neurosci. 2013 May;123(5):329-32.
PMID: 23270425
In this study, the researchers found that Parkinson’s Disease was also significantly associated to mumps, scarlet fever, influenza, and whooping cough as well as herpes simplex 1 infections. They found no association between Parkinson’s disease and Tuberculosis, measles or chickenpox though.
This result raises the tantalizing possibility that other viruses may also be involved with the onset of Parkinson’s disease (it should be added though that this study was based on only 110 people with Parkinson’s (compared with 220 controls) in one particular geographical location (Belgrade, Serbia)).
So different viruses may cause Parkinson’s disease?
We are not saying that either, but we would like to see more research on this topic.
And the situation may actually be more complicated than we think.
Recently, it has been reported that previous infection with flaviviruses (such as dengue) actually enhances the effect of Zika virus infect (Click here to read more on this). That is to say, a prior infection by one particular virus may exacerbate the infection of another virus. It could be that a previous infection by one virus increases that chance that a later infection by another virus – a particular combination of viral infections – may result in Parkinsonian symptoms (we are simply speculating here).
Add to this complicated situation, the sheer number of unknown viruses. It is estimated that there are a minimum of 320,000 mammalian viruses still awaiting discovery (Click here for the source of this statistic), thus it is possible that additional unknown viruses may be involved with disease initiation for conditions like Parkinson’s disease.
A gang of unknown thieves in the night perhaps?
So what does it all mean?
Summing up: last week a new study was published that supported previous results that Hepatitis C viral infections could increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease. The results are important because they replicate previous findings from a different population of people.
The findings do not immediately mean that people with Hepatitis C are going to develop Parkinson’s disease, but it does suggest that they may be more vulnerable. The findings also suggest that more research is needed on the role of viral/infectious agents in the development of Parkinson’s disease.
We would certainly like to see more research in this area.
The banner for today’s post was sourced from Youtube

Fascinating, isn’t it? There are some other links omitted from this introduction. For example, the Liver is inseparable from the Gall BLadder, except in disease conditions. How many PWPs have had their GB removed?
Just recently we had the crisis, especially in the UK, of Mad COw disease, making prions a household word.
Younger people may only have seen anthrax in Western movies but it occurred in Somerset in the early 1950s…. plus the rabbit population was infected with a virus… Considering this on presentation with a neurological disorder, say 20-40 years later, was, probably, overlooked.
LikeLike
Hi David,
Thanks for your comment, glad you found the post interesting. I have absolutely no idea regarding the GB removals. I’m not sure anyone has ever investigated it (vagotomies and appendectomies yes, but GB?).
I think it will be interesting to watch what happens to the prevalence of PD when a Hepatitis C vaccine becomes available. That will be a good test for part of this viral theory I suppose.
Kind regards,
Simon
LikeLike
I have been diagnosed with Parkinson’s Disease since 2015 (symptomatic 2011) and first predominately affecting right side but spreading to both sides. Intriguing the comments about GB removals. I had chronic cholecytitis and acute pancreatitis prior to gall bladder removal with decades of gastrointestinal problems pre GB removal. Given papers read on inflammatory diseases (I also have ankylosed spondylitis) and possible multifaceted causes of PD with gut flora being significant – it has always been an association I think relevant between gut, liver, gall bladder, pancreas and inflammatory conditions and onset of PD.
LikeLike
Simon,
The information that you convey is really appreciated. This virus trail seems pretty hot, but ultimately overwhelming. If Parkinson’s is triggered by commonly known viruses or maybe even by who knows how many yet unidentified viruses, what hope is there for prevention, a vaccine? Presently, it would seem that treatments aimed at foiling the pathology of alpha-synuclein protein are the best hope.
I follow the reports coming out of the protein immunotherapy development efforts of Prothena-Roche and Affrin and hopefully await the opportunity for approved therapy. Prothena has reported great success in the early phase trials for toxicity, side-effects, safety, etc. They are moving into phase II with their PRX002, this year.
Their latest study involved 80 Parkinson’s patients and the “results demonstrated rapid and dose-dependent reduction of free serum alpha-synuclein, the potential disease-causing protein in Parkinson’s Disease.” What I would like to know is did the participants in the trial experience any relief from the trial dosing?
Bill Jenkins
LikeLike
Hi Bill,
Appreciate the comment and your thoughts.
While I hope and pray that the immunotherapy approaches (Affiris & Prothena) will come through for us (ultimately putting me out of a job), I would still like to know what the causal agent/event is in this condition. Why do we get this insidious build up of proteins like alpha synuclein? Why the selective loss of cells in the brain? Why the asymmetry in the onset of motor symptoms? A viral influence could be a good fit in this situation.
I also don’t think an unidentified viral combo represents an unsurmountable challenge. A first step could be conducting a ‘virscan’ study on a large group of people with/without Parkinson’s disease (virscan is a blood test of one’s viral infection history – http://www.nhs.uk/news/2015/06June/Pages/New-blood-test-for-viral-infections-shows-promise.aspx). This would indicate any obvious candidates/combinations. An alternative approach could be DNA sequencing of post mortem brain tissue from people with/without Parkinson’s and looking at viral genomic material. Our brains harbour many dormant viruses (eg. chicken pox is still in there if you had it as a kid). The problem is finding the funding for such large studies that may not have a clear answer at the end (they are called ‘fishing trips’ in the research world).
It will certainly be interesting to see what happens with PRX002 in the next phase of the testing.
Kind regards,
Simon
LikeLike
Dear Stacey,
Thank you for your comment on the Science of Parkinson’s website. Unfortunately we don’t allow comments that advertise products or treatments on the site to avoid ethical and conflict of interest situations. For this reason, we can’t allow your message to be posted on the site. We hope you understand. Kind regards,
Simon
LikeLike