|
# # # # The first post at the start of each year on the SoPD website has traditionally tried to provide an overview or some context on where things are in the search for ‘disease modifying’ therapies for Parkinson’s. Previous editions of the “Road Ahead” posts have become dangerously overloaded, unwieldy, chaotic one-page beasts, so this year we are shifting to a multi-post format, which will hopefully provide the reader with less of a burdensome shopping list of novel therapies and more of a digestible piece of information (famous last words – be warned, this is still a very long post!). In this first post, we will look at the latest developments that have resulted from the biology associated with Parkinson’s-related genetic risk factors (this is a long post – click here if you would like to skip the introduction and go straight to the table of contents) # # # # |
 A future historian? Source: Inc
A future historian? Source: Inc
When future academics sit down to write the history of the condition that we currently know of as “Parkinson’s”, they may well look upon 1997 as a key turning point for what came next.
Why 1997? What happened then? And what came next?
On the morning of 27th June, 1997, the prestigious scientific journal ‘Science’ went to press, highlighting a research report that would change the world of Parkinson’s forever.
And I am not exaggerating here – the impact of the study was (and still is) truly profound.
The paper reported the discovery of tiny variations in a region of human DNA that scientists refer to as the “alpha synuclein” gene, and it explained that these genetic errors could significantly increase one’s risk of developing Parkinson’s. The scientists had made this finding across large Italian and Greek families that exhibited very high incidences of Parkinson’s (Click here to read a previous SoPD post on this discovery):

Title: Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease.
Authors: Polymeropoulos MH, Lavedan C, Leroy E, Ide SE, Dehejia A, Dutra A, Pike B, Root H, Rubenstein J, Boyer R, Stenroos ES, Chandrasekharappa S, Athanassiadou A, Papapetropoulos T, Johnson WG, Lazzarini AM, Duvoisin RC, Di Iorio G, Golbe LI, Nussbaum RL.
Journal: Science. 1997 Jun 27;276(5321):2045-7.
PMID: 9197268
And then – remarkably just two months later – the results of another study were published in the scientific journal ‘Nature’ that would further cement alpha synuclein’s place in Parkinson’s research.
In this second research paper, the investigators showed that a particular protein was highly enriched in “Lewy bodies” – dense spheres of protein inside of cells that are one of the characteristic features of the Parkinsonian brain. That protein was the very same one that is produced by the instructions provided by the alpha synuclein gene:
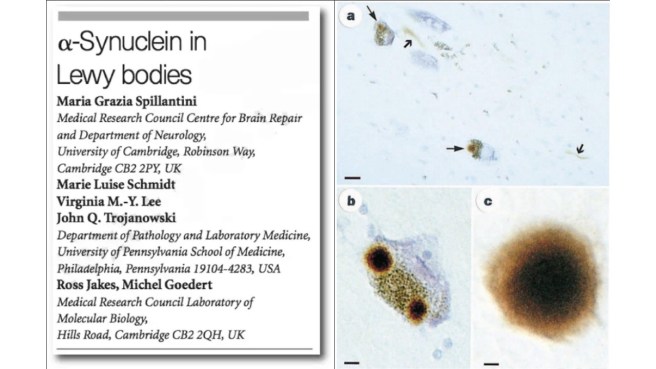 Title: Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies.
Title: Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies.
Authors: Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M.
Journal: Nature. 1997 Aug 28;388(6645):839-40.
PMID: 9278044
And so it was that alpha synuclein became ‘public enemy #1’ in the world of Parkinson’s research. After decades of research, scientist finally had their ‘foot in the door’ in terms of the biology that could potentially be underlying the condition.
What came next can only be described as a ‘gold rush’ in Parkinson’s research, with genetic risk factors in other regions of DNA suddenly being associated with Parkinson’s. In 1998, genetic variations in one called the “PARKIN” gene were discovered, then in 2003 it was the turn of “DJ-1″, followed the year after by the “LRRK2″ and “PINK1″ genes.
Today we know of approximately 80 genetic regions believed to be influencing the risk of developing Parkinson’s:
 Nalls et al (2019). Source: PMC
Nalls et al (2019). Source: PMC
While all of this research focused on variation in our DNA does not mean that Parkinson’s is a genetic condition (please note that these variations are only found in about 15-20% of the PD affected community and infer vulnerability rather than certainty), the truly crucial aspect of these discoveries has been learning about the associated biology.
What do you mean by “associated biology”?