|
Parkinson’s is a neurodegenerative condition. This means that cells in the brain are being lost over time. Any ‘cure’ for Parkinson’s is going to require some form of cell replacement therapy – introducing new cells that can replace those that were lost. Cell transplantation represents one approach to cell replacement therapy, and this week we learned that the Japanese regulatory authorities have given the green light for a new cell transplantation clinical trial to take place in Kyoto. This new trial will involve cells derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (or IPS cells). In today’s post we will discuss what induced pluripotent stem cells are, what previous research has been conducted on these cells, and what we know about the new trial. |

Source: Glastone Institute
The man in the image above is Prof Shinya Yamanaka.
He’s a rockstar in the biomedical research community.
Prof Yamanaka is the director of Center for induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Research and Application (CiRA); and a professor at the Institute for Frontier Medical Sciences at Kyoto University.
But more importantly, in 2006 he published a research report that would quite literally ‘change everything’.
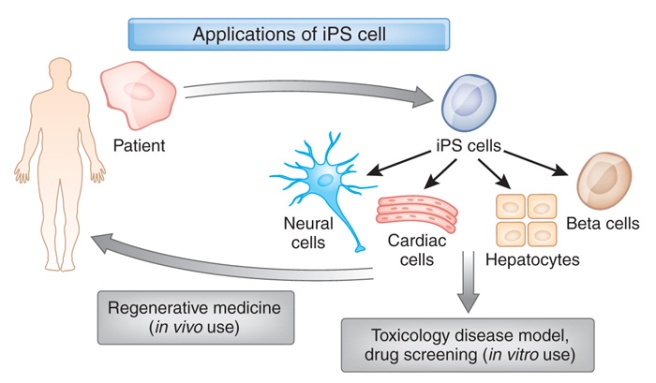
In that report, he demonstrated a method by which someone could take a simple skin cell (called a fibroblast), grow it in cell culture for a while, and then re-program it so that it would transform into a stem cell – a cell that is capable of becoming any kind of cell in the body.
The transformed cells were called induced pluripotent stem (IPS) cell – ‘pluripotent’ meaning capable of any fate.
It was an amazing feat that made the hypothetical idea of ‘personalised medicine’ suddenly very possible – take skin cells from anyone with a particular medical condition, turn them into whatever cell type you like, and then either test drugs on those cells or transplant them back into their body (replacing the cells that have been lost due to the medical condition).
Personalised medicine with IPS cells. Source: Bodyhacks
IPS cells are now being used all over the world, for all kinds of biomedical research. And many research groups are rushing to bring IPS cell-based therapies to the clinic in the hope of providing the long sort-after dream of personalised medicine.
This week the Parkinson’s community received word that the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) – the Japanese regulatory agency that oversees clinical trials – have agreed for researchers at Kyoto University to conduct a cell transplantation trial for Parkinson’s, using dopamine neurons derived from IPS cells. And the researchers are planning to begin their study in the next month.
In today’s post we are going to discuss this exciting development, but we should probably start at the beginning with the obvious question:
What exactly is an IPS cell?